Do Airplanes Have Windshield Wipers? This question often arises among aviation enthusiasts and curious passengers alike. While many might assume that every vehicle designed for travel through the skies would be equipped with such a common feature, the reality is quite different. This article explores the functionality and necessity of windshield wipers on airplanes, addressing common misconceptions and providing insights into aircraft safety measures during adverse weather conditions.
Understanding the design and engineering choices that lead to the absence of windshield wipers on most commercial aircraft is essential for grasping how pilots maintain visibility in challenging weather. The aerodynamic shape of an aircraft minimizes water accumulation on the windshield, allowing for clearer visibility without the need for traditional wipers. Additionally, the high speeds at which airplanes travel help to disperse rain and snow, further reducing the necessity for such devices.
Pilots utilize various techniques and technologies to ensure clear visibility, even without traditional windshield wipers, during flights in rain, snow, or fog. One of the primary methods is the use of windshield heating systems, which are crucial for preventing ice accumulation and maintaining visibility.
Windshield heating systems work by warming the glass, which helps to melt any snow or ice that may form. This technology is particularly important during takeoff and landing when weather conditions can change rapidly. The embedded electrical elements in heated windshields distribute heat evenly across the surface, ensuring that visibility is preserved during cold or icy conditions.
- Enhances safety by reducing the need for physical wipers.
- Minimizes maintenance issues associated with mechanical wipers.
- Allows for uninterrupted visibility during critical phases of flight.
Modern aircraft are equipped with advanced avionics that assist pilots in navigating through poor weather conditions. These systems make windshield wipers less necessary than in smaller aircraft. For instance, weather radar systems provide real-time data on weather patterns, allowing pilots to make informed decisions about flight paths and avoid severe weather.
Aircraft are designed with multiple safety features to handle inclement weather, ensuring that pilots can operate safely even in challenging conditions. The aerodynamic design of aircraft helps to minimize the impact of rain and wind, allowing for safer operations without the need for windshield wipers.
Pilots undergo extensive training to handle various weather scenarios, equipping them with the skills needed to maintain safety and visibility, regardless of the aircraft’s equipment. This training includes simulations of adverse weather conditions, allowing pilots to practice their response strategies without actual risk.
In addition to training, pilots rely on standard operating procedures that dictate how to respond to various weather conditions. These procedures are developed based on extensive research and historical data, ensuring that pilots are prepared for any situation they may encounter.
In summary, while airplanes do not typically feature windshield wipers, they are equipped with sophisticated technologies and safety measures that ensure pilots maintain visibility during adverse weather. Through the use of heated windshields, advanced avionics, and rigorous training, pilots are well-prepared to navigate challenging conditions, making air travel safer than ever.

Why Don’t Most Airplanes Have Windshield Wipers?
When considering the design of commercial aircraft, one might wonder, This question leads us to explore the engineering decisions that prioritize safety and functionality in aviation. Understanding these choices is crucial for grasping how pilots maintain visibility during challenging weather conditions.
Commercial aircraft are meticulously designed with various features to ensure optimal visibility, even without traditional windshield wipers. The absence of wipers is not a mere oversight but a result of advanced engineering practices aimed at enhancing safety and performance.
Pilots rely on a combination of technology and techniques to ensure their visibility remains clear, despite the absence of windshield wipers. Here are some of the primary methods:
- Windshield Heating Systems: These systems play a vital role in preventing ice and snow accumulation on the glass. By warming the windshield, they effectively melt any frost or ice that might obstruct the pilot’s view.
- Advanced Avionics: Modern aircraft are equipped with sophisticated avionics that assist pilots in navigating through poor weather conditions, making wipers less necessary compared to smaller aircraft.
- Weather Radar: Real-time weather radar systems provide pilots with critical information about weather patterns, allowing them to make informed decisions and avoid severe conditions.
Windshield heating systems are essential for maintaining visibility during cold weather. These systems utilize embedded electrical elements that distribute heat evenly across the windshield surface. This technology not only prevents ice formation but also ensures that pilots can maintain a clear view during critical flight phases.
Utilizing heated windshields offers several advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: By eliminating the need for physical wipers, pilots can focus more on flying and less on maintaining visibility.
- Reduced Maintenance: Fewer mechanical components mean less potential for malfunction and lower maintenance costs over time.
- Uninterrupted Visibility: Heated windshields provide consistent clarity, especially during takeoff and landing, which are critical moments in any flight.
The aerodynamic design of aircraft is another factor that minimizes the impact of rain and wind. By streamlining the aircraft’s shape, engineers have reduced drag and improved overall performance, allowing for safe operations without the need for windshield wipers.
Extensive training prepares pilots to handle various weather scenarios. They learn to utilize all available technology and techniques to maintain safety and visibility, no matter the conditions. This training is crucial, as it equips pilots with the skills to navigate through rain, snow, or fog, ensuring that they can operate safely even in challenging environments.
In summary, while the absence of windshield wipers on most commercial aircraft may seem unusual, it is a testament to the innovative engineering and design principles that prioritize safety and efficiency. By leveraging advanced technologies and training, pilots can effectively maintain visibility and ensure a safe flying experience.
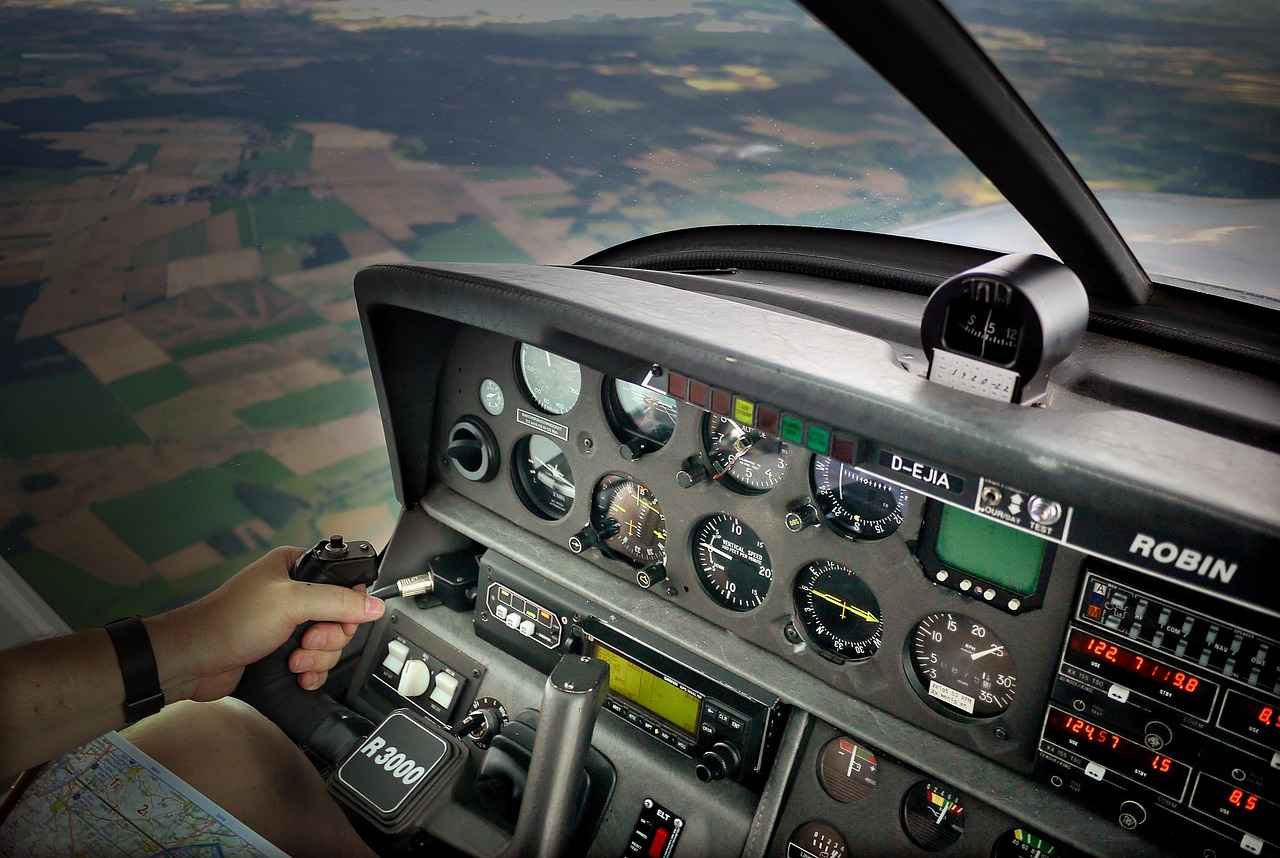

How Do Pilots Maintain Visibility in Adverse Weather?
In the realm of aviation, ensuring visibility during adverse weather conditions is paramount for safety. While many may wonder about the absence of traditional windshield wipers on commercial aircraft, pilots have developed a range of techniques and technologies to maintain clear sightlines, even in challenging scenarios such as rain, snow, or fog.
During flights in inclement weather, pilots rely on a combination of advanced systems and training to ensure they can navigate safely. Here are some of the key methods employed:
- Windshield Heating Systems: These systems are essential for preventing ice accumulation on the cockpit glass. By warming the windshield, they help to melt any snow or ice that may form, ensuring that visibility is preserved.
- Advanced Avionics: Modern aircraft are equipped with sophisticated avionics that assist pilots in navigating through poor weather conditions. These systems provide crucial data and alerts that help pilots make informed decisions.
- Weather Radar: Utilizing weather radar systems allows pilots to receive real-time information about weather patterns. This data enables them to avoid severe weather and adjust flight paths accordingly.
- Enhanced Cockpit Displays: Advanced displays provide pilots with a comprehensive view of their surroundings and weather conditions, allowing for better situational awareness without reliance on traditional wipers.
Windshield heating systems are a vital component in maintaining visibility during cold weather. These systems function by embedding electrical elements within the glass, which distribute heat evenly across the surface. As a result, any snow or ice that forms is melted away, providing pilots with an unobstructed view.
Heated windshields offer numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: By eliminating the need for physical wipers, heated windshields reduce the risk of mechanical failure, which can occur with traditional wiper systems.
- Minimized Maintenance: Fewer moving parts mean less wear and tear, leading to lower maintenance costs and increased reliability.
- Uninterrupted Visibility: Pilots can maintain clear visibility during critical phases of flight, such as takeoff and landing, without worrying about wiper functionality.
Pilot training plays a crucial role in ensuring safety during adverse weather. Pilots undergo extensive training to handle various scenarios, equipping them with the skills needed to maintain visibility and safety, regardless of the aircraft’s equipment. This training includes:
- Simulator Training: Pilots practice flying in simulated adverse weather conditions, allowing them to develop strategies for maintaining visibility and making safe decisions.
- Real-World Experience: Experienced pilots learn to rely on their judgment and the tools available to them, gaining insights into how to best navigate through challenging weather.
- Continuous Learning: Ongoing education and training updates ensure that pilots stay informed about the latest technologies and best practices for flying in adverse conditions.
Weather detection systems have revolutionized how pilots approach inclement weather. These systems provide critical information about weather patterns and allow pilots to make informed decisions about flight paths. By understanding the severity and location of storms, pilots can avoid dangerous areas and maintain safety throughout the flight.
In summary, while traditional windshield wipers are not commonly found on commercial aircraft, pilots have access to a variety of advanced technologies and training that ensure they can maintain visibility during adverse weather. Through the use of windshield heating systems, sophisticated avionics, and comprehensive training, pilots are well-equipped to navigate safely through challenging conditions.
The Role of Windshield Heating Systems
Windshield heating systems play a vital role in ensuring safety and visibility for pilots, especially in adverse weather conditions. These systems are designed to combat the challenges posed by ice and snow accumulation on the windshield, which can severely impair a pilot’s ability to see the outside environment. In this section, we will delve deeper into how these systems operate, their benefits, and their significance in aviation safety.
Windshield heating systems utilize embedded electrical elements within the glass itself. When activated, these elements generate heat that spreads evenly across the surface of the windshield. This process effectively melts any ice or snow that may have formed, ensuring that the pilot maintains clear visibility.
- Enhanced Safety: By preventing ice accumulation, these systems significantly reduce the risk of visibility loss during critical flight phases.
- Reduced Maintenance: The absence of traditional windshield wipers minimizes potential mechanical issues, leading to lower maintenance costs.
- Improved Efficiency: Heated windshields allow for uninterrupted visibility, enabling pilots to focus on navigation and communication without distractions.
Unlike conventional windshield wipers, which can become less effective in heavy snow or ice, heated windshields provide a consistent solution to visibility challenges. Wipers can also obstruct the view and may require regular maintenance, whereas heated systems are generally more reliable and require less upkeep.
Windshield heating systems are designed to operate effectively in various weather conditions, including extreme cold. However, during particularly severe weather, such as heavy snowfall or ice storms, pilots may still need to rely on other technologies and techniques to ensure safety.
Modern aircraft are equipped with a range of advanced technologies that work in tandem with windshield heating systems:
- Weather Radar: This technology provides real-time updates on weather conditions, allowing pilots to navigate around severe weather.
- De-icing Systems: These systems can be used in conjunction with windshield heaters to prevent ice build-up on critical aircraft surfaces.
- Advanced Avionics: Enhanced cockpit displays provide pilots with vital information about flight conditions, further assisting in maintaining visibility.
While windshield heating systems are highly effective, they do have limitations. For instance, if the ice is too thick or if the system is malfunctioning, pilots may still experience visibility issues. Therefore, it is essential for pilots to be trained in various scenarios to handle such situations effectively.
As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in windshield heating systems, including enhanced energy efficiency and faster heating capabilities. Research is ongoing to develop materials that can provide even better performance in extreme conditions.
In summary, windshield heating systems are an essential component of modern aviation safety. By preventing ice accumulation and ensuring clear visibility, these systems allow pilots to navigate challenging weather conditions with confidence. Their integration with other technologies further enhances their effectiveness, making them a preferred choice over traditional windshield wipers.
How Do Heated Windshields Work?
Heated windshields are an innovative solution designed to enhance visibility for drivers and pilots alike, particularly in adverse weather conditions. By employing advanced technology, these windshields ensure that ice and snow do not obstruct the view, which is crucial for safe operation. Understanding how heated windshields work provides insight into their significance in modern vehicles and aircraft.
Heated windshields incorporate embedded electrical elements within the glass. These elements are strategically placed to distribute heat evenly across the entire surface of the windshield. This technology is particularly effective in preventing the accumulation of ice and snow, which can severely impair visibility.
The process begins when the vehicle’s heating system activates the embedded wires or conductive films. These elements generate heat, which radiates outward, warming the glass. This warming effect is crucial for melting any ice or snow that may have formed on the windshield. The even distribution of heat ensures that there are no cold spots, which could lead to uneven melting and potential visibility issues.
In icy or snowy conditions, maintaining clear visibility is essential for safe driving or flying. Heated windshields enhance safety by:
- Reducing the need for physical wipers: With a heated windshield, the reliance on traditional wipers is minimized, which can lead to fewer mechanical failures.
- Improving visibility: By preventing ice buildup, pilots and drivers can maintain a clear line of sight, crucial for navigating through challenging weather.
- Enhancing comfort: A warm windshield can also contribute to a more comfortable cabin environment, as it helps to reduce fogging and condensation.
Yes, there are various types of heated windshields available:
- Conductive Film: This type uses a thin layer of conductive material applied to the glass surface to generate heat.
- Embedded Wires: These are fine wires embedded within the glass itself, creating a grid pattern that heats the windshield when electricity flows through them.
- Hybrid Systems: Some advanced systems combine both methods for optimal heating efficiency.
While traditional windshield wipers are effective for removing rain and light snow, they are often less efficient in severe conditions. Heated windshields provide a more reliable solution by:
- Eliminating mechanical failure: Wipers can wear out or malfunction, especially in extreme weather, whereas heated systems are generally more reliable.
- Reducing maintenance: Fewer moving parts mean less wear and tear, leading to lower maintenance costs over time.
Despite their advantages, heated windshields do have some limitations:
- Cost: They are typically more expensive to manufacture and replace than standard windshields.
- Power Consumption: The heating elements require electrical power, which can be a concern in energy-sensitive situations.
In summary, heated windshields represent a significant advancement in automotive and aviation safety technology. By providing consistent heat distribution across the glass surface, they ensure that visibility is maintained in cold and icy conditions. This technology not only enhances safety but also reduces the need for traditional wipers, leading to lower maintenance and improved reliability.
Benefits of Heated Windshields
In the realm of aviation, ensuring visibility during flight is of utmost importance, particularly in adverse weather conditions. One of the innovative solutions that have emerged in modern aircraft design is the use of heated windshields. These advanced systems play a vital role in maintaining clear visibility, enhancing safety, and reducing the dependency on traditional windshield wipers.
- Enhanced Safety: Heated windshields significantly improve safety by preventing ice and snow accumulation. This is crucial during critical phases of flight, such as takeoff and landing, where visibility is paramount.
- Reduced Maintenance Issues: By minimizing the need for physical wipers, heated windshields lower the chances of mechanical failure. This not only reduces maintenance costs but also enhances the reliability of the aircraft.
- Uninterrupted Visibility: The continuous heating of the windshield ensures that pilots maintain a clear view of their surroundings, even in challenging weather. This uninterrupted visibility is essential for making timely and informed decisions during flight.
Heated windshields operate through a series of embedded electrical elements that distribute heat evenly across the glass surface. This technology allows for the quick melting of ice or snow, ensuring that pilots can see clearly without the need for wipers. The heating elements are designed to activate automatically when temperatures drop, providing a seamless solution to visibility challenges.
- Less Mechanical Complexity: Traditional wipers can suffer from wear and tear, leading to potential failures. Heated windshields eliminate this mechanical complexity, providing a more reliable solution.
- Improved Aerodynamics: The absence of wipers contributes to better aerodynamics. This design choice helps enhance fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance.
- Increased Pilot Confidence: Knowing that visibility is maintained without the need for wipers allows pilots to focus more on flying rather than dealing with potential mechanical issues.
Yes, heated windshields contribute to environmental sustainability in aviation. By enhancing fuel efficiency through improved aerodynamics and reducing maintenance-related waste, these systems align with the industry’s goals to minimize its environmental footprint. Furthermore, the use of electric heating elements is often more energy-efficient compared to the energy consumed by traditional wiper systems.
The aviation industry is continually evolving, and the technology behind heated windshields is no exception. Future innovations may include smart heating technologies that adjust the temperature based on real-time weather conditions, further optimizing performance and safety. Additionally, advancements in materials science could lead to even more efficient heating solutions that enhance durability and effectiveness.
In summary, the benefits of heated windshields extend far beyond mere convenience. They play a crucial role in enhancing safety, reducing maintenance issues, and providing uninterrupted visibility during critical flight phases. As technology continues to advance, we can expect heated windshields to become an even more integral part of aircraft design, ensuring that pilots can navigate through any weather condition with confidence.
Advanced Avionics and Technology
In the realm of aviation, advanced avionics play a crucial role in enhancing safety and efficiency, particularly in adverse weather conditions. While smaller aircraft often rely on traditional windshield wipers to maintain visibility, larger commercial airplanes are equipped with sophisticated technology that minimizes the need for such mechanical solutions.
Advanced avionics refer to the integrated electronic systems used in modern aircraft for navigation, communication, and monitoring. These systems provide pilots with vital information and assist in decision-making, especially during challenging weather scenarios.
Modern aircraft utilize a variety of avionics systems to navigate through poor weather. One of the primary tools is the weather radar, which provides real-time data on precipitation, storms, and turbulence. This allows pilots to adjust their flight paths proactively, avoiding severe weather and ensuring passenger safety.
Advanced avionics enhance situational awareness by displaying critical flight data on multifunction displays. This information includes altitude, speed, and weather conditions, allowing pilots to make informed decisions quickly. By having a comprehensive view of their surroundings, pilots can maintain control and visibility without the reliance on windshield wipers.
- Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS): These systems alert pilots to potential collisions with terrain, particularly in low visibility conditions.
- Traffic Collision Avoidance Systems (TCAS): This technology helps prevent mid-air collisions by providing pilots with alerts about nearby aircraft.
- Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B): ADS-B technology allows aircraft to share their position with air traffic control and other aircraft, enhancing situational awareness.
During flights, pilots continuously monitor the data provided by these advanced avionics systems. For instance, if the weather radar indicates heavy precipitation ahead, pilots can choose to alter their altitude or reroute the flight path to avoid the worst of the storm. This proactive approach significantly reduces the reliance on windshield wipers, which are less effective in severe weather.
While advanced avionics greatly enhance safety, they are not infallible. Pilots must be trained to interpret the data accurately and make decisions based on the information available. Additionally, technical malfunctions, although rare, can occur, necessitating a thorough understanding of backup systems and manual flying skills.
As technology continues to evolve, the role of advanced avionics in aviation will only expand. Innovations such as artificial intelligence and machine learning may soon provide even more sophisticated tools for pilots, further enhancing safety and operational efficiency in adverse weather conditions. The integration of these systems not only makes flying safer but also reflects the ongoing commitment to improving aviation technology for the benefit of all.
Weather Radar and Detection Systems
Weather radar and detection systems play a pivotal role in modern aviation, providing critical real-time information about weather conditions that pilots face during flight. These systems enable pilots to make informed decisions regarding their flight paths, thereby enhancing safety and efficiency.
Weather radar systems utilize advanced technology to detect precipitation, storm systems, and other meteorological phenomena. By sending out radio waves, these systems can identify the location, intensity, and movement of weather patterns. This real-time data is essential for pilots as it allows them to anticipate and respond to changing weather conditions.
One of the primary benefits of weather radar is its ability to provide early warnings about severe weather. Pilots can use this information to alter their flight paths, avoiding dangerous conditions such as thunderstorms, heavy rain, or turbulence. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of encountering hazardous weather during flight.
The integration of weather radar into cockpit displays ensures that pilots have immediate access to vital weather information. This real-time data empowers pilots to make quick decisions, such as changing altitude or rerouting, to maintain safety. Moreover, pilots can communicate with air traffic control to coordinate safe navigation through or around adverse weather.
Modern weather radar systems come equipped with sophisticated features that enhance their functionality:
- Color-Coded Displays: These displays help pilots quickly assess the severity of weather conditions, with different colors indicating varying levels of precipitation and turbulence.
- Predictive Capabilities: Some systems can forecast weather patterns, allowing pilots to anticipate changes and adjust their flight plans accordingly.
- Integration with Other Systems: Weather radar can be integrated with other avionics, providing a comprehensive overview of flight conditions and enhancing situational awareness.
Pilot training includes extensive education on interpreting weather radar data. Understanding how to read and respond to radar information is crucial for maintaining safety in adverse weather. Pilots are trained to recognize patterns and make decisions based on the data presented, ensuring they can navigate safely even in challenging conditions.
In summary, weather radar and detection systems are essential tools in aviation, providing pilots with the information needed to navigate safely through adverse weather. By enhancing decision-making capabilities and allowing for real-time adjustments to flight paths, these systems significantly contribute to the overall safety and efficiency of air travel.

What Are the Safety Measures for Aircraft in Inclement Weather?
When it comes to aviation, safety is the top priority, especially during inclement weather. Aircraft are engineered with a multitude of safety features to navigate through challenging conditions such as heavy rain, snow, or fog. Understanding these measures can provide insight into how pilots maintain safety and operational integrity in adverse weather scenarios.
Aircraft are designed with several advanced technologies and systems that enhance safety during difficult weather conditions. These measures are critical in ensuring that pilots can operate safely, even when faced with the unpredictability of nature.
The aerodynamic design of aircraft plays a significant role in their performance during inclement weather. The shape and structure of an aircraft are optimized to minimize drag and maximize stability, even in turbulent conditions. For instance:
- Wing Design: Wings are crafted to generate lift efficiently, allowing for better control during adverse weather.
- Stability Features: Many aircraft are equipped with features that enhance stability, such as winglets that reduce turbulence.
Pilots undergo rigorous training that prepares them for various weather scenarios. This training includes:
- Simulation Training: Pilots practice flying in simulated adverse weather conditions to hone their skills.
- Emergency Procedures: Comprehensive training on how to react in emergencies ensures pilots are ready for any situation.
Furthermore, pilots are trained to use various instruments and technology to maintain situational awareness, which is crucial in low-visibility conditions.
Modern aircraft are equipped with advanced weather radar systems that provide real-time data on weather conditions. These systems allow pilots to:
- Identify Severe Weather: Pilots can detect thunderstorms, turbulence, and other hazardous conditions ahead of time.
- Make Informed Decisions: With accurate weather data, pilots can adjust their flight paths to avoid dangerous areas.
Although most commercial aircraft do not have traditional windshield wipers, they are equipped with heating systems that prevent ice and snow accumulation on the windshields. These systems work by:
- Embedded Electrical Elements: These elements heat the windshield surface evenly, ensuring clear visibility during cold weather.
- Enhanced Safety: By eliminating the need for physical wipers, these systems reduce maintenance issues and improve reliability.
Modern avionics technology plays a crucial role in enhancing flight safety during adverse weather. Aircraft are equipped with various systems that assist pilots in:
- Navigation: Advanced navigation systems help pilots chart safe courses through complicated weather patterns.
- Communication: Continuous communication with air traffic control provides pilots with updated weather information and guidance.
In conclusion, the combination of advanced aerodynamics, rigorous pilot training, sophisticated weather detection systems, windshield heating technology, and modern avionics all contribute to the remarkable safety of aircraft in inclement weather. These features ensure that pilots can operate effectively, maintaining safety and confidence even in the most challenging conditions.
Aircraft Design Considerations
The aerodynamic design of aircraft plays a crucial role in enhancing safety and performance, particularly during adverse weather conditions. One of the remarkable aspects of this design is its ability to minimize the impact of rain and wind. This innovative engineering allows aircraft to operate safely without the need for traditional windshield wipers, a feature often seen in automobiles.
Aerodynamics is the study of how air interacts with moving objects. In aviation, this principle is applied to create shapes that reduce drag and improve lift. The streamlined design of an aircraft helps in directing airflow smoothly over its surface, which significantly reduces turbulence caused by wind and rain. This design not only enhances fuel efficiency but also contributes to safer flight operations.
Rain and wind can pose significant challenges during flight. However, the aerodynamic shape of an aircraft is engineered to minimize these effects. For instance, raindrops are directed away from critical surfaces, ensuring that visibility and control are maintained. Additionally, the aircraft’s design allows it to cut through turbulent air, reducing the risk of encountering severe weather phenomena.
Modern aircraft are equipped with advanced systems to cope with adverse weather. These include:
- Weather Radar: Provides real-time data on weather patterns, allowing pilots to navigate around storms.
- De-icing Systems: Prevent ice accumulation on critical surfaces, ensuring safe operations during cold weather.
- Wing Design: Features such as winglets help improve stability and control in turbulent conditions.
The absence of windshield wipers in most commercial aircraft is a testament to the effectiveness of their design and technology. The combination of heating systems and advanced avionics ensures that pilots maintain clear visibility without the need for mechanical wipers. This not only simplifies maintenance but also reduces the weight of the aircraft, contributing to overall efficiency.
Pilots undergo rigorous training to handle various weather scenarios. They learn to rely on their instruments and advanced systems rather than traditional wipers. This training equips them with the skills necessary to make informed decisions, ensuring safety during challenging conditions.
In summary, the aerodynamic design of aircraft significantly enhances safety by minimizing the impact of rain and wind. This innovative approach, combined with advanced technology and pilot training, allows for safe operations without the reliance on windshield wipers. As aviation technology continues to evolve, the focus on safety and efficiency remains paramount, ensuring that air travel remains one of the safest modes of transportation.
Training and Procedures for Pilots
In the world of aviation, pilot training is a critical component that ensures safety and efficiency during flights. As pilots face various weather scenarios, their rigorous training equips them with the necessary skills to maintain visibility and safety, regardless of the aircraft’s equipment. This section delves into the extensive training and procedures that pilots undergo to handle adverse weather conditions effectively.
Pilots participate in comprehensive training programs that include both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This training covers:
- Ground School Education: Pilots learn about meteorology, understanding different weather patterns, and how they affect flight operations.
- Simulator Training: Advanced simulators allow pilots to experience various weather scenarios, including turbulence, thunderstorms, and low visibility, without leaving the ground.
- In-Flight Training: Real-world flying experience under the supervision of experienced instructors helps pilots apply their knowledge in practical situations.
Before and during flights, pilots utilize several tools and resources to assess weather conditions:
- Weather Briefings: Pilots receive detailed briefings that provide updated information on weather patterns along their flight route.
- Onboard Weather Radar: Modern aircraft are equipped with advanced radar systems that offer real-time data on precipitation and storm activity, helping pilots make informed decisions.
- Communication with Air Traffic Control: Continuous communication with air traffic controllers ensures that pilots stay informed about changing weather conditions and can adjust their flight paths accordingly.
In the absence of traditional windshield wipers, pilots rely on several techniques to ensure clear visibility:
- Utilizing Windshield Heating: Heated windshields prevent ice and snow buildup, maintaining clarity during cold weather.
- Adjusting Flight Altitude: Pilots may change altitude to fly above cloud cover or adverse weather, ensuring a smoother and clearer flight.
- Using Visual Cues: Pilots are trained to recognize visual cues and landmarks during flight, which helps them navigate even in low visibility conditions.
Unexpected weather changes can pose significant challenges, but pilots are trained to respond effectively:
- Emergency Procedures: Pilots are trained in emergency protocols to handle sudden weather changes, ensuring passenger safety.
- Decision-Making Skills: Training emphasizes the importance of quick decision-making, allowing pilots to adapt to unforeseen circumstances.
- Team Coordination: Effective communication and coordination with co-pilots and crew are essential during challenging weather conditions.
Overall, the extensive training and procedures that pilots undergo prepare them to face a variety of weather scenarios confidently. This preparation is crucial for maintaining safety and ensuring that flights can operate smoothly, even under challenging conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Do airplanes really need windshield wipers?
No, most airplanes don’t have windshield wipers because they use advanced technologies like heated windshields and weather radar to maintain visibility. These systems help pilots see clearly without the need for traditional wipers.
- How do heated windshields work?
Heated windshields feature embedded electrical elements that evenly distribute heat across the glass. This prevents ice and snow from accumulating, ensuring pilots have a clear view during cold weather.
- What safety measures are in place for flying in bad weather?
Aircraft are designed with aerodynamic features that reduce the impact of rain and wind. Additionally, pilots receive extensive training to handle various weather conditions, ensuring they can operate safely even in challenging environments.
- Can pilots still see during heavy rain or fog?
Yes! Pilots utilize advanced avionics and weather detection systems to navigate through poor visibility conditions. These technologies provide real-time data, allowing pilots to make informed decisions about their flight paths.
- Are there any maintenance issues with heated windshields?
Heated windshields generally require less maintenance compared to traditional wipers. Since they eliminate the need for moving parts, there are fewer mechanical failures, enhancing overall safety and reliability.